Iron Phosphate Coating
Iron phosphate coating stands as a pivotal process in the nature of advanced surface treatments, serving a multitude of industries with its impressive ability to prime and protect metal surfaces. It’s the fusing of chemistry and engineering, a silent guardian against the inevitable wear and tear that metal products face.
Exploring Iron Phosphate Coating
Iron phosphate coating is a chemical treatment applied to metal surfaces to enhance their corrosion resistance and paint adhesion properties. It’s a conversion coating that transforms the metal substrate into a layer of non-metallic, insoluble phosphate crystals, which forms a solid base for further finishes or as a standalone protection against environmental factors.
Technical Process Of Iron Phosphate Coating
The application of iron phosphate coating is a synthesis of science and precision engineering, ensuring the utmost in metal protection.
Cleaning And Pre-Treatment
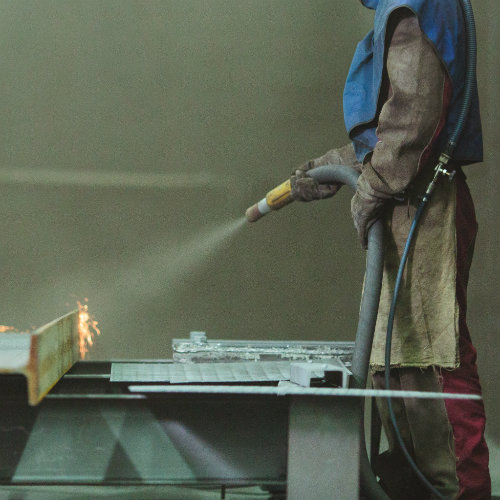
The first step in applying an iron phosphate coating is the thorough cleaning and pre-treatment of the metal surface. This stage is critical as any contaminants left on the metal can impede the coating’s ability to form correctly. Industrial-grade solutions are employed to degrease and remove debris, ensuring a clean slate for coating application.
This pre-treatment not only purifies the surface but also begins the micro-etching process that optimizes the metal for the coating to come.
Applying The Coating
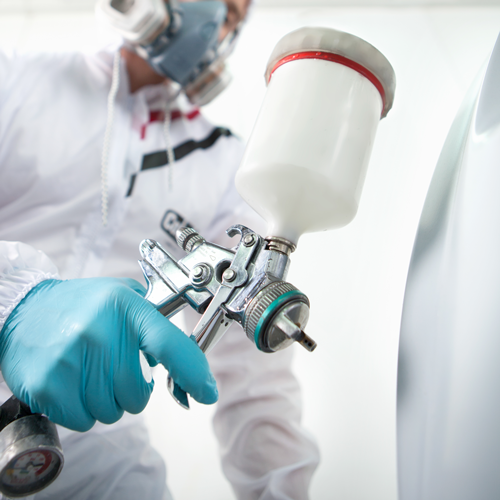
Once the metal is clean, the iron phosphate coating is meticulously applied. The application method is chosen based on the shape of the parts, their intended use, and the complexity of their design. Immersion techniques are often preferred for their ease of coating complex geometries uniformly, while spraying can be adapted to cover large batches or sizes efficiently. During this phase, the coating reacts chemically with the metal substrate to form a layer of iron phosphate crystals, providing superior protection and a perfect foundation for finishes like paint or powder coating.
Rinsing And Sealing
Following the application, the next critical step is rinsing and sealing. The rinsing process removes excess coating and balances the surface pH, while sealing enhances the protective properties of the coating.
This sealant layer is vital as it fills any microscopic pores in the coating, forming an additional barrier against corrosion, ensuring the longevity of the coating’s protective properties. A high-quality sealant aids in optimizing surface adherence for additional finishing layers, such as paint.
Drying And Curing
The final phase is drying and curing the coating, which solidifies the chemical bond and ensures the coating’s full protective capabilities are realized. Proper drying and curing are essential for the longevity and effectiveness of the phosphate coat.
A carefully controlled environment is used for this stage to prevent any inconsistencies that could compromise the coating. Once cured, the iron phosphate layer exhibits excellent resistance qualities, providing a durable base for further treatment or as a standalone protection.
Innovative Techniques In Applying Iron Phosphate Coatings
Automation In Coating Application
The use of automation in the application of iron phosphate coatings is transforming the industry. Automated systems allow for a level of precision that is virtually unmatched, consistently delivering uniform coatings across all treated parts. This technological advancement is not only enhancing the quality of the coating but also increasing throughput and efficiency in production lines.
Customized Application Methods
The ability to adapt to the unique needs of each project is crucial in iron phosphate coating applications. Customized application methods are designed to accommodate different shapes, sizes, and complexities of metal parts. This versatility is key to achieving an optimal coating because each part has unique attributes that may require a specific approach, be it immersion, spraying, or a combination of techniques.

Quality Assurance Protocols
Maintaining high standards of quality is integral to the success of iron phosphate coating applications. After the coating is applied, parts undergo thorough quality assessment protocols to check for consistency, thickness, and completeness of the coat. This evaluation is done using a combination of visual inspections and advanced testing equipment, ensuring that every part meets precise performance criteria.
Post-Coating Treatments
Beyond the initial application of iron phosphate coatings, additional treatments can be employed to further enhance the protective qualities of the coated parts. These post-coating treatments, such as oiling or passivation, provide additional barriers against environmental factors like moisture and salt, which could potentially lead to corrosion.
Benefits Of Choosing Iron Phosphate Coating Services
Selecting iron phosphate coating services is a strategic decision that comes with a wealth of advantages.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Iron phosphate coatings are your first line of defense in guarding metal components against the relentless assault of corrosion. This protective layer actively resists rust and degradation, a feature especially crucial in challenging environments where exposure to moisture, salt, or chemicals is common.
By significantly bolstering the metal’s resilience, iron phosphate coatings ensure that your components maintain their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal over a much longer period, thus reducing the potential for costly downtimes or repairs.
Improved Paint Adhesion
A well-applied iron phosphate coating isn’t just a barrier; it’s a bridge to better adhesion for paints and finishes. It creates an ideal surface that finishes can cling to more effectively, drastically minimizing the chances of peeling or flaking over time.
Enhanced adhesion translates into a longer-lasting and visually impeccable finish, which is critical in consumer-facing products or in industries where precision coatings, such as aerospace and automotive, are required.
Environmental Benefits
Iron phosphate coatings stand out not only for their performance but also for their lower environmental impact, a point of pride for service providers like Valence. These coatings are often recognized for their environmental benefits, as they typically involve a less toxic process compared to other metal finishing methods.
Cost-Effectiveness
The practicality of iron phosphate coatings extends to the economical domain. This surface treatment presents a cost-effective option by elongating the life span of metal components and thus curtailing the need for frequent replacements.
Valence’s Commitment To Exceptional Iron Phosphate Coating Results
Leading-Edge Facilities
These advanced operational plants enable them to handle a wide spectrum of detailed projects with finesse and precision. Equipped with the latest machinery and automation capabilities, we consistently delivers coatings that meet the high-performance demands of the aerospace, automotive, and defense industries.
Trained And Experienced Technicians
Through a combination of rigorous training programs and hands-on experience, our professionals have honed their abilities to execute each project with exacting standards. Our in-depth understanding of the nuances involved in different coating processes allows them to navigate any challenges with confidence, ensuring that every project is completed to the highest quality.

Frequently Asked Questions
What industries commonly use iron phosphate coatings?
Iron phosphate coatings are used across several industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, and heavy machinery due to their ability to enhance corrosion resistance and paint adhesion.
Can iron phosphate coatings be applied to all metal surfaces?
They are most effective on iron, steel, and galvanized surfaces. However, with the right pre-treatment, they can also be applied to aluminum and other metals.
How long does an iron phosphate coating last?
The durability of the coating depends on the environment and the coated object’s usage. Generally, it provides long-term protection, and when combined with a topcoat, its lifespan can extend significantly.
Are there different types of iron phosphate coatings?
Yes, there are variations such as heavy zinc phosphate and light iron phosphate coatings, each suited for different protective or adhesion requirements.
Why is pre-treatment important before applying iron phosphate coatings?
Pre-treatment cleans and prepares the metal surface, ensuring that the coating adheres properly and performs as expected, which is vital for the coating’s effectiveness.
What property of iron phosphate coatings makes them environmentally friendly?
Iron phosphate coatings often involve less hazardous chemicals compared to other metal finishing processes, aligning with environmentally conscious manufacturing practices.
Does the iron phosphate coating thickness affect its performance?
Yes, the coating thickness can influence its corrosion resistance and should be tailored to the application’s specific requirements.
Do iron phosphate coatings require special care or maintenance?
While inherently durable, coated objects may benefit from occasional cleaning to maintain their protective properties, especially in harsh environments.
What are some of the post-coating treatments available for iron phosphate coated parts?
Post-coating treatments like oiling or passivation can offer additional corrosion protection and improve the efficacy of the iron phosphate coating.
How can I tell if iron phosphate coating is right for my application?
Evaluating the environmental conditions and desired outcomes of your project can help determine if this coating method is suitable for your needs.
Painting Services
Primer
Primer, also known as undercoat, is the preparatory coating that can be used to enhance the bond strength of a topcoat and/or improve the corrosion resistance of a part. Applying primer is a crucial first step to the lasting results.
Fuel Tank Coating
Fuel tank coating is a specialty coating applied to the interior of aircraft fuel tanks that protects against corrosion from fuel contaminants. The coating allows fuel tanks to meet industry standards for longer durations.
Adhesive Bond Primer
Topcoat
Topcoat is the final coating on a part often used for cosmetic purposes. However, it often has application specific properties, such as reflectivity, conductivity, etc. The topcoat provides durability and resistance to harmful materials that will cause parts to deteriorate.
Anti-Chafe
Anti-Chafe topcoats are specific coatings that are primarily used on surfaces where abrasion resistance, low friction and impact resistance are required to reduce chafing and wear. This specific topcoat serves as a defense in harmful environments.
Dry Film Lube
Dry film lube is a dry lubricant coating that reduces friction on surfaces sliding against each other. It offers operation at higher temperatures than other lubricants.
Sol-Gel
Sol-Gel is a process of creating metal oxides when applied to a part using metal alkoxides. The sol-gel is in high demand as it allows adhesive bonding of titanium and corrosion resistant alloys.
Zinc Spray
Zinc spray, or zinc chromate spray is a primer with corrosion inhibiting properties, commonly used on aluminum aircraft or spacecraft components. It is a high quality aerospace plating technique.
Digital Masking
Valence performs all of these services to the highest degree of care, with approvals for most prime and military specifications. Our products and services significantly enhance safety, long-term use, and consistency in the aerospace industry. View our specs here.
Painting Capability Sizes
| Valence Eastman | L | Valence Wichita | L | Valence Grove | L | Valence Los Angeles | L | Valence Seattle | L | Valence Everett | L | Valence Garden Grove | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bond Primer | 20' | Bond Primer | 16' | Bond Primer | 24' | Bond Primer | 27' | Bond Primer | 6' | Bond Primer | 30' | Bond Primer | 10' |
| Dry Lube | 20' | Dry Lube | 16' | Dry Lube | 10' | Dry Lube | 27' | Dry Lube | 2.5' | Dry Lube | 30' | Paint | 10' |
| Fuel Tank Coating | 20' | Fuel Tank Coating | 16' | Fuel Tank Coating | 24' | Fuel Tank Coating | 27' | Fuel Tank Coating | 6' | Fuel Tank Coating | 30' | ||
| Primer | 20' | Primer | 16' | Primer | 24' | Primer | 27' | Prime and Topcoat | 6' | Primer | 30' | ||
| Topcoat | 20' | Sol Gel | 16' | Topcoat | 24' | Topcoat | 27' | Sol Gel | 4' | Topcoat | 30' | ||
| Sol Gel | 20' | Topcoat | 24' | Sol Gel | 24' | Sol Gel | 27' | Sol Gel | 30' | ||||
| Zinc Spray | 12' |
Painting & Spray Coating News
What Are Thermal Control Coatings (TCC) For Satellites?
As satellites venture through the unforgiving expanse of space, they face a formidable challenge: the extreme temperatures that fluctuate between scorching heat and icy cold. To conquer this cosmic thermal battleground, satellites enlist the aid of a remarkable ally:...
Thermal Control Coatings: A Necessary Component For Satellites
Discover why thermal control coatings are essential for safeguarding satellites against extreme temperatures and may guarantee their optimal performance…
Passivation Standards ASTM A967
Stainless steel, having found applications in different industries is an important part of our daily lives. In the aerospace and even many manufacturing industries, stainless steel has found application and is a very important material. It is known to have better...
What Is Passivation: The Secret To Long-Lasting Metal Protection
Understand the ABCs of passivation and learn how it extends the life of metal components by protecting them from corrosion and oxidation …